Abstract
Background: Acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality following hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Corticosteroids are the current standard of care for initial therapy; however, 35%-60% of patients become refractory to treatment, and prolonged systemic exposure is associated with burdensome toxicity and morbidity. Ruxolitinib, an oral selective Janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK2 inhibitor approved for steroid-refractory (SR)-aGVHD in adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older, is an effective and well-tolerated treatment. Primary results from the pivotal REACH2 trial demonstrated a significantly higher response rate with ruxolitinib vs best available therapy (BAT). However, the impact of the timing of ruxolitinib initiation on efficacy after diagnosis of SR-aGVHD needs further investigation.
Methods: REACH2 (NCT02913261) was a multicenter, randomized, open-label phase 3 study in which patients aged ≥12 years with grade II-IV SR-aGVHD were randomized to receive ruxolitinib 10 mg twice daily or investigator-selected BAT. This post hoc analysis examined overall response rate (ORR [complete response (CR) + partial response (PR)]) at Day 28, best overall response (BOR) at any time, and duration of response (DOR) between early (within 0-3 days of SR-aGVHD), late (4-6 days for ruxolitinib vs ruxolitinib), very late (≥7 days), and late-and-very-late (≥4 days for ruxolitinib vs BAT analyses) study treatment initiation. Subgroups were defined based on time from SR-aGVHD to randomization. DOR was defined as time from first response to aGVHD progression or the addition of new systemic therapy for aGVHD; competing risks were the onset of chronic GVHD, or death without progression of aGVHD. For the ruxolitinib vs BAT analysis, odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI for ORR (or BOR) were calculated using the stratified Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test. For the ruxolitinib vs ruxolitinib analysis, OR and 95% CI for ORR (or BOR) were calculated using Wald confidence limits. DOR was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method.
Results: Overall, 154 patients were randomized to ruxolitinib (n=112, 42, and 24 for early, late-and-very-late [≥4 days], and very late, respectively) and 155 to BAT (n=115, 40, and 22 for early, late-and-very-late, and very late). Median age ranged from 48.5-55 years between subgroups, and most patients were male (range between subgroups; 40.9%-75.0%). Most patients had grade II or III aGVHD at randomization (range between subgroups, 12.5%-50.0% for grade II; 40.2%-54.8% for grade III), with skin and lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract organs most frequently involved at randomization (range between subgroups, 40.9%-66.1% [skin]; 59.8%-75.0% [lower GI]). Mean time from diagnosis of aGVHD grade ≥II to randomization was 19.8-46.0 days between subgroups.
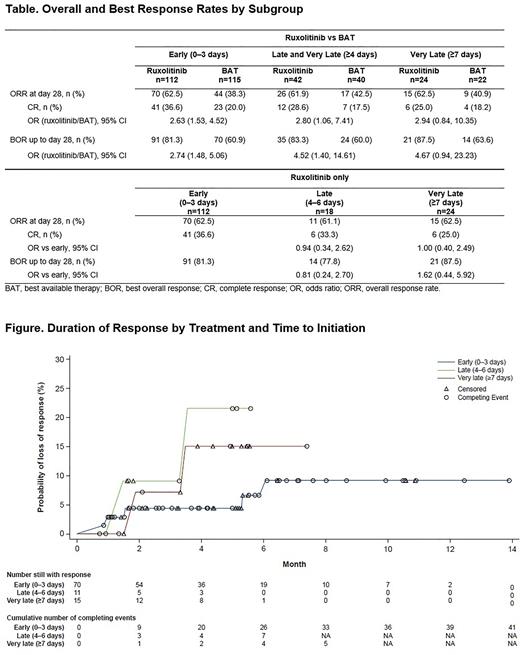
Ruxolitinib was superior to BAT in early (OR, 2.63 [95% CI: 1.53, 4.52]) and late-and-very-late treatment (OR, 2.80 [95% CI: 1.06, 7.41]) and was numerically greater in very late treatment only (OR, 2.94 [95% CI: 0.84, 10.35]; Table). CR was higher in ruxolitinib vs BAT in early treatment (OR, 2.63 [95% CI: 1.53, 4.52]). Similar results were observed for BOR of CR or PR up to Day 28 (Table). Mean (IQR) DOR for ruxolitinib vs BAT was 141.5 (63.0-186.0) vs 99.3 (38.5-148.0) days for early treatment, 107.3 (50.0-156.0) vs 91.7 (52.0-129.0) days for late-and-very-late treatment, and 123.7 (64.0-166.0) vs 87.1 (48.0-129.0) days for very late treatment.
No differences were observed between ruxolitinib time to treatment subgroups for ORR or BOR (Table). DOR represented as probability of loss of response over time between ruxolitinib-treated groups is presented in the Figure. There is a trend toward higher likelihood of loss of response with late and very late initiation of ruxolitinib vs early.
Conclusions: These data demonstrate that ruxolitinib provides clinical benefit vs BAT, regardless of treatment delay time after onset of SR-aGVHD. There was a trend toward higher remissions with early initiation of ruxolitinib (≤3 days of SR-aGVHD diagnosis). Responses with early ruxolitinib treatment were more durable than responses achieved after late or very late treatment, reinforcing the importance of early treatment initiation in SR-aGVHD.
Disclosures
Socié:Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Lecture Fees, Research Funding; Xenikos: Consultancy, Other: Lecture Fees, Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Consultancy, Other: Lecture Fees, Research Funding. Xue:Incyte Corporation: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Bhatt:Incyte Corporation: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Galvin:Incyte Corporation: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Mohty:Oncopeptides: Honoraria; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer,: Honoraria; GSK: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal